Our practice offers patients highly specialized urologic care using the most up-to-date methods and equipment including minimally invasive robotic, laparoscopic, endoscopic, percutaneous, microscopic and open surgical techniques. We treat a wide variety of urologic conditions affecting the Kidneys, Adrenal Glands, Ureters, Bladder, Prostate Gland, and Genital Organs.
Urology & Urological Surgery
Kush Patel, MD, FACS
Our Approach
Our Office
Board Certified Urologist
Robotic Assisted Surgery
Accepting New Patients
To schedule an appointment please call – 704-871-9818
“I treat my patients as I would my own family,” Dr. Kush Patel told me as we met in his quiet office. “My goal with each person I see is to empower them to participate in their healthcare goals. Using understandable, clear laymen’s terms is critical when I explain conditions and treatment options. I Inform my patients what’s going on with their body so they can make a considered, appropriate decision. I’m their guide.”
“Dr Patel is a wonderful urologist. He listens and truly wants to get to the bottom of the problem and figure ways to help you.” –Kate
“Great Doctor. A very caring person. He takes his time and explains them to you. Thank you Dr. Patel!” –Judy
Meet Our Team
Our Location
STATESVILLE
702 Hartness Rd
Statesville, NC 28625
Directions
704-871-9818 Phone
704-495-3626 Fax
MOORESVILLE
359 Williamson
Mooresville, NC 28117
Directions
Phone: 704-871-9818
Dr. Patel offers no-scalpel vasectomy. This procedure can often be done in less than 25 minutes. Local anesthesia is used to numb the skin. An instrument is used to make two ¼ inch openings in the scrotal skin. The vas (left and right) are cut, tied and cauterized. Then dissolvable suture is used to close the openings.
A bladder scan is used to determine a patient’s post void residual (amount of urine left in bladder after a patient urinates). An ultrasound probe is placed over the lower abdomen. This takes only a few seconds.
This test produces images that are used to asses organs and structures within the pelvis. An ultrasound probe is placed over different regions the lower abdomen and mild pressure is applied. This test takes less than 5 minutes.
This procedure allows the urologist to determine if a male patient has prostate cancer and also to stage prostate cancer. During this procedure an ultrasound probe is placed into the patient’s rectum to help visualize correct biopsy location. Local anesthesia is then given to make the patient more comfortable. A spring-loaded needle quickly enters the prostate gland and removes a tissue sample. 12 samples are taken from different areas of the prostate gland. This procedure generally takes less than 5 minutes. Biopsy results are given to the patient in person about 2 weeks after biopsy.
This is a procedure that allows the urologist to examine the lining of your bladder and your urethra (tube that carries urine out of your body). A thin flexible tube with lens (cystoscope) is inserted into your urethra and advanced into your bladder. In male patients the urologist is also able to view the prostatic urethra (portion of the urethra that runs through the prostate gland). This procedure generally takes 4-5 minutes. Prior to this procedure local anesthetic is placed at the urethral opening to make the patient more comfortable.
Cystoscopy For Removal of Uteral Stent
This involves a cystoscopy (see description above) but while the urologist is examining the bladder he/she is then able to grasp the string at the end of the urethral stent and remove stent by pulling stent out through the urethral opening. Removal of the stent often takes less than 30 seconds.
If you’ve tried several treatments for bladder control problems without success, don’t lose hope. There is no single bladder control treatment that works for everyone, and sometimes it takes time to find the one that works for you.
This procedure is used to treat overactive bladder. During this procedure a cystoscope is inserted into your bladder (see description of cystoscopy above). The urologist then injects Botox into specific sites of the bladder wall. This procedure takes about 5 minutes.
These tests assess the bladder and urethra in their ability to store and release urine. Urodynamics are often used to explain urinary incontinence, urinary frequency and urinary urgency. This test involves the placement of small flexible catheters in the bladder and rectum. The catheters assess for pressure, and the bladder catheter also allows for the filling of the bladder with saline. The bladder is slowly filled with saline as the catheters assess for changes in pressure. The patient is also checked for urinary leakage. All catheters are removed at the completion of the test. The results and treatment options are discussed with the patient after the procedure. This procedure often takes 20-30 minutes.
What are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and acid salts that form in concentrated urine. Passing them through the urinary tract can be painful, but they typically do not cause lasting damage. The most common symptom is intense pain, usually in the side of the abdomen, often accompanied by nausea.
Renal lithotripsy, also known as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), is a non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller pieces that can pass through the body. Here’s how it works:
- A machine called a lithotripter generates shock waves.
- An X-ray is used to accurately target these shock waves onto the kidney stone.
- The shock waves travel through the body, skin, and tissue, breaking the stone into small fragments.
This procedure can also be used to break up stones in the bladder or the ureter, the tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove kidney stones that are too large to pass naturally or do not respond to other treatments. During PCNL, a small puncture is made through the skin and into the kidney or upper ureter to access and remove the stones. This procedure is typically recommended for large, hard, or complex kidney stones located near the pelvic area or that have not been successfully treated with methods like shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy.
A ureteral stent, or ureteric stent, is a thin tube inserted into the ureter to prevent or treat obstruction of the urine flow from the kidney.
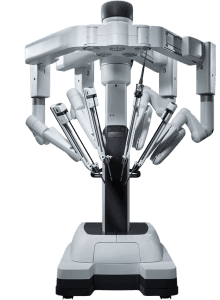 Dr. Kush Patel is trained in using the Da Vinci robotic system. The Da Vinci robot is a sophisticated surgical system used to perform minimally invasive surgeries. The surgeon operates the robot from the console, controlling the robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments. The system translates the surgeon’s hand movements into precise micro-movements of the instruments.
Dr. Kush Patel is trained in using the Da Vinci robotic system. The Da Vinci robot is a sophisticated surgical system used to perform minimally invasive surgeries. The surgeon operates the robot from the console, controlling the robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments. The system translates the surgeon’s hand movements into precise micro-movements of the instruments.
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also known as hormone therapy, is a treatment for prostate cancer that reduces testosterone levels to slow the growth of cancer cells. While testosterone supports the health of a normal prostate, it can also promote the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. ADT is often the first-line treatment for advanced prostate cancer and can be used in conjunction with radiation therapy or after a radical prostatectomy.
Brachytherapy, also known as internal radiation therapy, is a treatment that involves placing a radioactive source inside or near a tumor to destroy cancer cells. The source, which can be a seed, wire, disc, ribbon, or capsule, delivers a concentrated dose of radiation directly to the cancer cells, minimizing damage to nearby healthy tissue. The procedure is usually painless.
A radical nephrectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the complete removal of a kidney, along with adjacent tissues such as the adrenal gland, lymph nodes, and a portion of the ureter.
An adrenalectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing either one or both adrenal glands. Typically, it is conducted to address large tumors, excessive hormone production, or concerns regarding potential malignancy. The specific approach to adrenalectomy varies based on individual circumstances.
Pyeloplasty is a surgical procedure performed to address a blockage at the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ), which is the pathway that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. When the UPJ becomes obstructed, urine flow is hindered, potentially causing kidney pain, infections, kidney stones, and loss of kidney function. During pyeloplasty, the surgeon removes the blockage to restore normal urine flow towards the bladder.
Ureterolithotomy is a surgical procedure used to extract kidney stones lodged in the ureter. This operation can be conducted either laparoscopically or through an open surgical approach.
Understanding BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, or BPH, is a condition in which the prostate enlarges as men get older. BPH is a very common condition that affects over 40 million Americans and over 500 million aging men worldwide. Over 40% of men in their 50s and over 70% of men in their 60s have BPH . While BPH is a benign condition and unrelated to prostate cancer, it can greatly affect a man’s quality of life.
As the prostate enlarges, it presses on and blocks the urethra, causing bothersome urinary symptoms such as:
- Frequent need to urinate both day and night
- Weak or slow urinary stream
- A sense that you cannot completely empty your bladder
- Difficulty or delay in starting urination
- Urgent feeling of needing to urinate
- A urinary stream that stops and starts
If you suffer from the above symptoms, you are not alone. BPH is the leading reason men visit a urologist.
You can measure the severity of your BPH symptoms by taking the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) questionnaire.
What is the UroLift System?
Treatment with the UroLift® System uses a minimally invasive approach that provides rapid relief and recovery of BPH symptoms. It is an earlier treatment option can get men off BPH medications and avoid major surgery. The goal of the UroLift System treatment is to relieve symptoms so you can get back to your life and resume your daily activities.
The UroLift® System treatment has demonstrated a significant improvement in quality of life for patients compared to medications. The UroLift® System is the only BPH procedure shown not to cause new and lasting erectile or ejaculatory dysfunction*, while being a safe and effective treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to BPH.
For men with BPH seeking a normal, uncompromised life, Aquablation therapy offers a minimally invasive, effective solution for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) caused by BPH. Using robotic precision, Aquablation therapy delivers lasting results with a low risk of complications, empowering you to live confidently on your terms.



